Theodore Lowe, Ap #867-859 Sit Rd, Azusa New York
We are available 24/ 7. Call Now. (888) 456-2790 (121) 255-53333 example@domain.com
Reconstructive
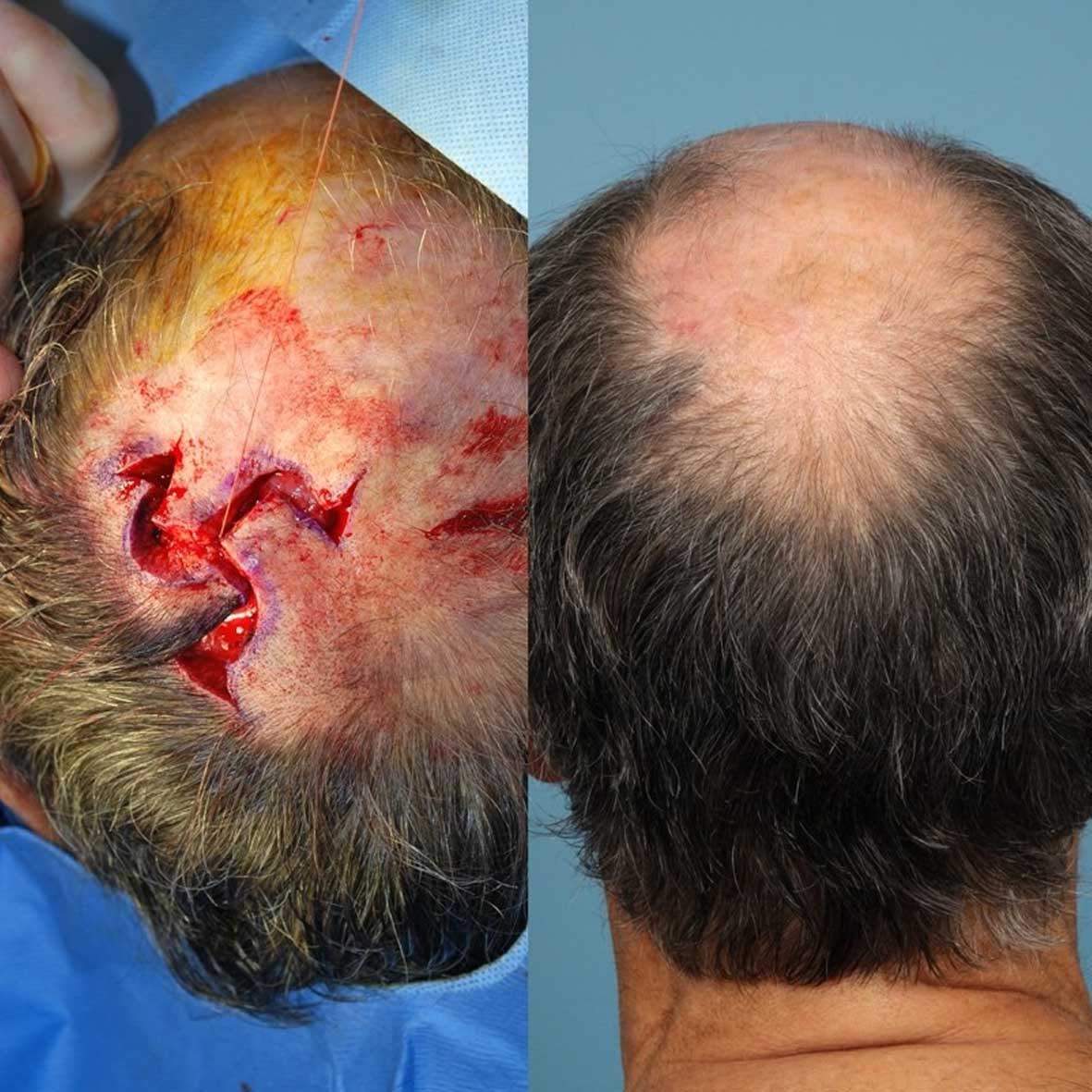
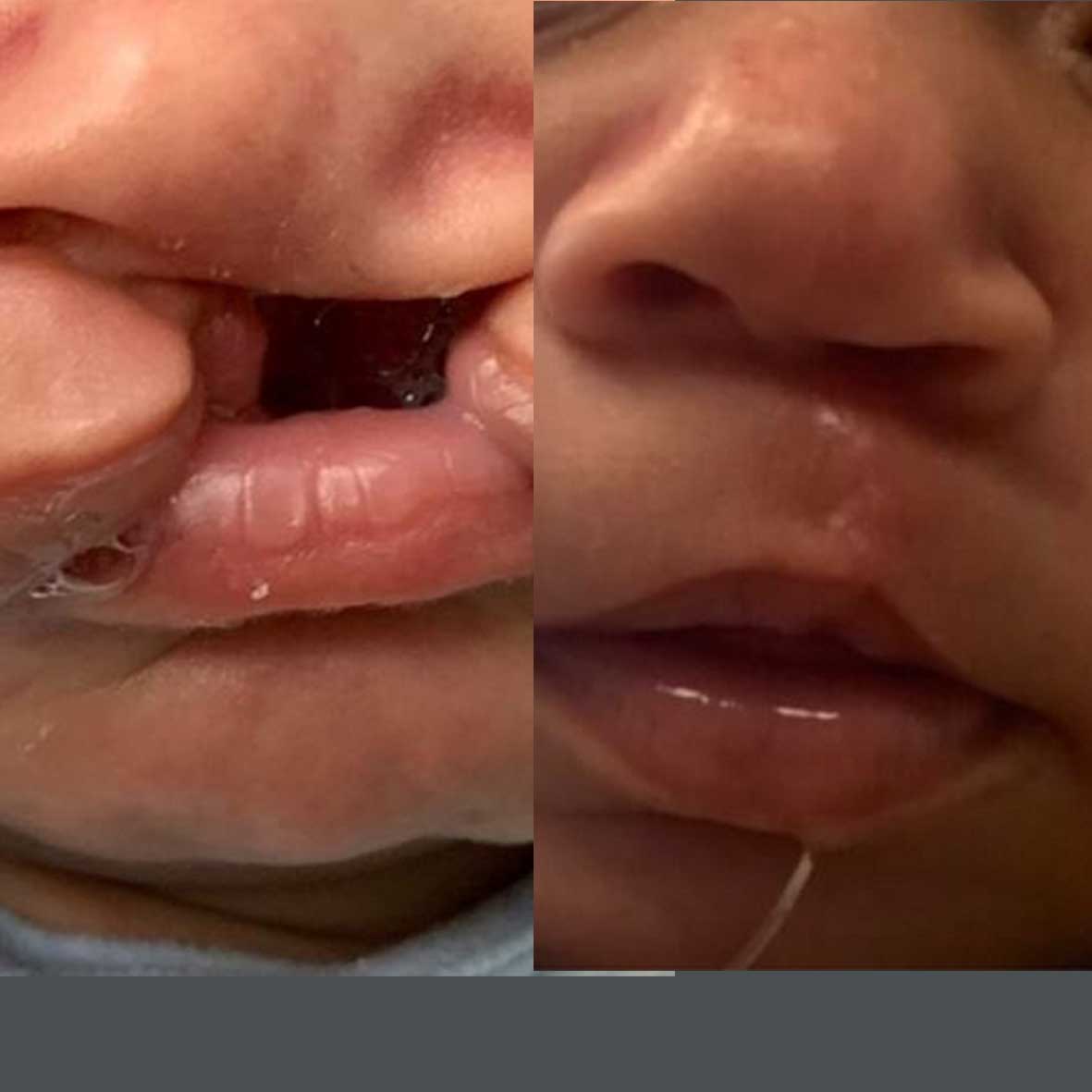

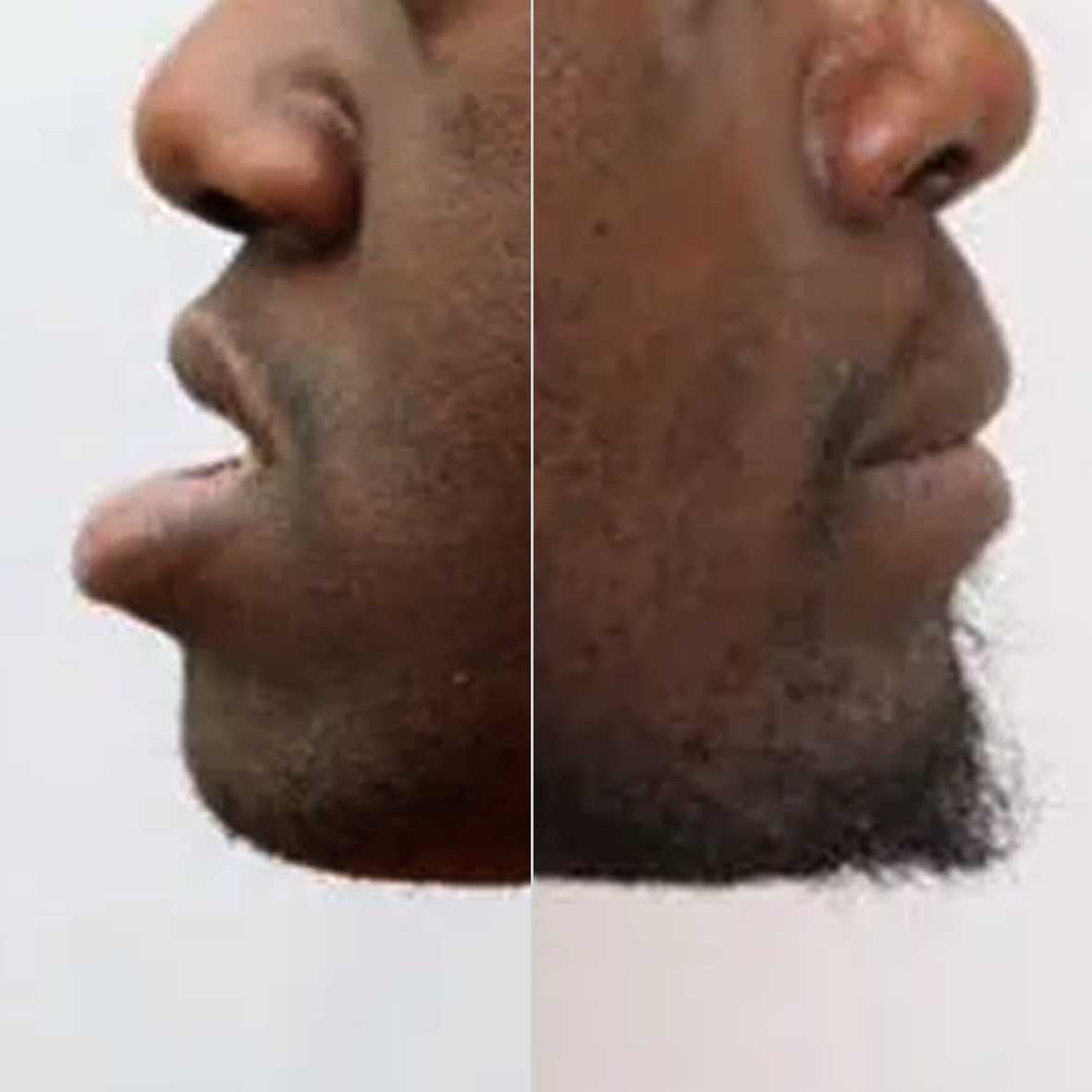


Body contouring refers to a series of cosmetic surgical procedures that aim to reshape and improve the overall appearance of the body. It typically involves removing excess skin and fat to create a more toned, sculpted look.
Some common types of body contouring procedures include:
• Liposuction: This procedure involves removing excess fat from various parts of the body, such as the abdomen, hips, thighs, and arms.
• Tummy tuck: Also known as abdominoplasty, this procedure involves removing excess skin and fat from the abdomen and tightening the muscles to create a flatter, more toned appearance.
• Body lift: This involves removing excess skin and fat from multiple areas of the body, such as the abdomen, thighs, and buttocks, to create a more contoured appearance.
• Arm lift: This procedure involves removing excess skin and fat from the upper arms to create a more toned and sculpted appearance.
• Thigh lift: This procedure involves removing excess skin and fat from the thighs to create a more toned and defined look.
Body contouring can help to improve the body’s overall proportions and create a more youthful, toned appearance. It can also boost confidence and self-esteem. However, it is important to note that body contouring is not a weight loss procedure and should not be used as a substitute for a healthy lifestyle.


- FGM
- J PLASMA
- GASTRIC BALOON
- PHARMACY AND LAB
- PLATELET-RICH PLASMA
- WEIGHT-LOSS PROGRAM
- NANO-FAT FOR ACNE SCARS
- RECONSTRUCTION SURGERY
- PAINLESS HAIR REMOVAL - DEMA LASER
